When screening patients for potential sleep-related breathing disorders, three common visual screening tools are used; The Friedman Tongue Position, The Mallampati Index, and The Friedman Tonsil Index. Most undergraduate dental education does not cover these three screening tools. If you will be referring your patients to physicians to help get undiagnosed Obstructive Sleep Apnea patients diagnosed you need to become acquainted with them. Below is a guide to help familiarize yourself with the indexes.
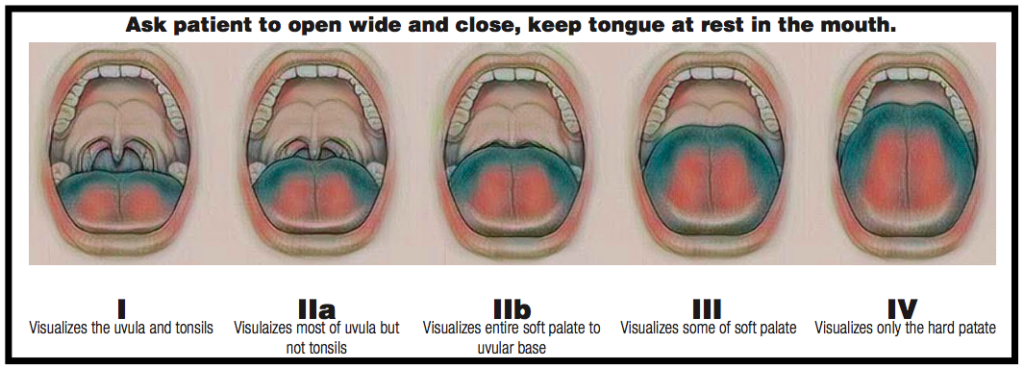
The Friedman Tongue Position (FTP) is a standardized way to classify a hypopharyngeal obstruction. The FTP also called the Modified Mallampati, evaluates the tongue’s position relative to the tonsils/pillars, uvula, soft palate, and hard palate. It is based on the Mallampati system but uses a neutral tongue position. To evaluate, ask the patient to open their mouth widely, a minimum of 5 times. This repetition allows you to observe the most consistent position of the tongue. If you find an FTP of III or IV, the patient is almost assuredly suffering from OSA.
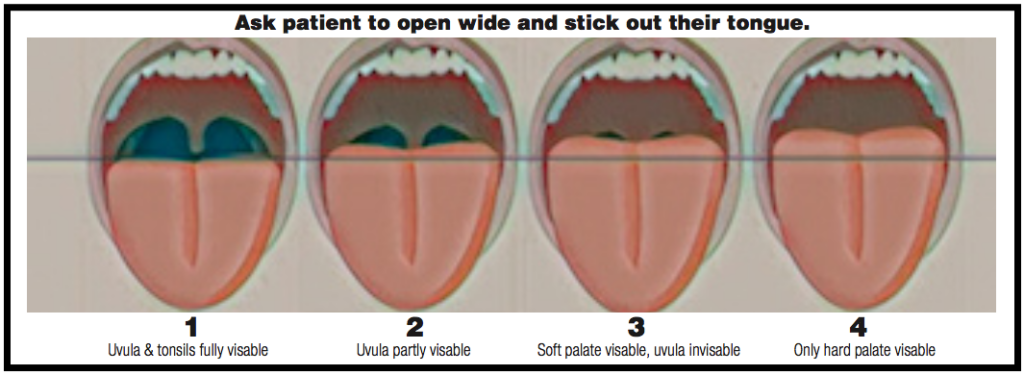
Anesthesiologists designed the Mallampati index to determine the difficulty of intubating a patient for surgery. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine includes the Mallampati index as one of the screening tools for physicians and other health care providers to use to determine the risk for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. During your oral cancer screening, ask the patient to open wide and stick out their tongue. The way to classify the patient is based on how much the patient’s tongue blocks the airway. Class III and Class IV are considered high risk for OSA. Please see the adjacent picture as a visual reference for the four classifications of Mallampati.
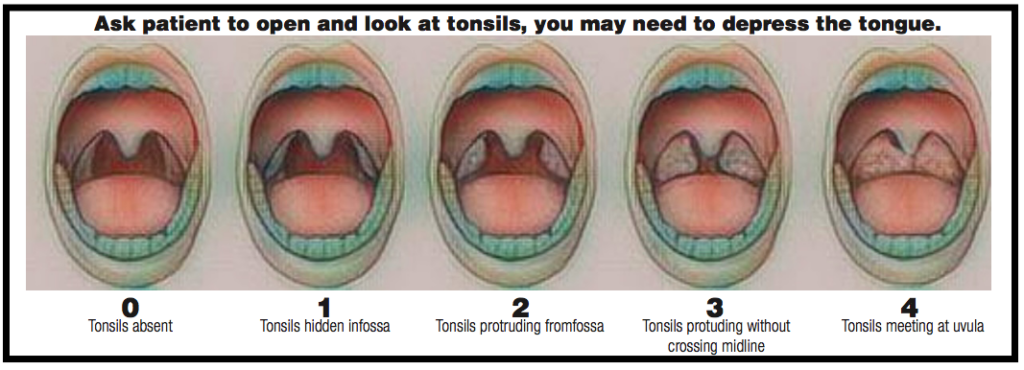
The Friedman Tonsil Index is a tool that physicians sometimes use to determine the risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. It is commonly believed that it is predictive in children and less useful in adults. The grading system consists of a scale from 0 to 4. Grade 0 denotes a complete absence of lymphoid tissue on the tongue base. Grade 1 is defined as lymphoid tissue scattered over the tongue base. Grade 2 represents lymphoid tissue covering the entirety of the tongue base with limited vertical thickness. Grade 3 consists of significantly raised lymphoid tissue surrounding the tongue base’s entirety, approximately 5–10 mm in thickness. Grade 4 represents lymphoid tissue 1 cm or more in thickness, rising above the epiglottis’ tip.

If you are interested in referring a patient to Dr. Christina Cairns please visit my practice website with the following link, to download a referral sheet, electronically refer or just learn more about Colorado Springs Sleep Apnea & TMJ Solutions: Sleepishealthy.com
